Understanding EBIT margin or Earnings Before Interest and Taxes margin, is crucial for assessing a company’s operational efficiency and profitability. In this article, we’ll explore some common questions about EBIT margin and provide clear, easy-to-understand answers to help readers grasp this important financial metric.
Contents
What is EBIT margin?
- EBIT margin is a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by expressing its earnings before interest and taxes as a percentage of revenue.
- It indicates how much profit a company generates from its operations relative to its total revenue.
How is EBIT margin calculated?
- EBIT margin is calculated by dividing a company’s EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) by its total revenue and multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage.
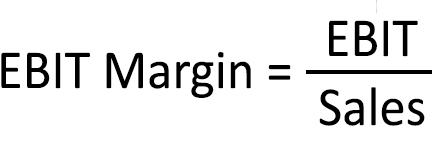
Why is EBIT margin important for businesses?
- EBIT margin is important for businesses because it provides insights into their operational efficiency and profitability.
- By analyzing EBIT margin, businesses can assess how effectively they are generating profits from their core operations, independent of financing and tax considerations.
How does EBIT margin differ from net profit margin?
- EBIT margin differs from net profit margin in that it excludes interest expenses and taxes from the calculation.
- Net profit margin, on the other hand, represents the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after deducting all expenses, including interest and taxes.
What factors can influence EBIT margin?
- Several factors can influence EBIT margin, including changes in revenue, operating expenses, cost of goods sold, and other operating costs.
- Improvements in operational efficiency, cost control measures, and revenue growth initiatives can lead to higher EBIT margins, while factors such as increased competition or economic downturns may result in lower EBIT margins.
Conclusion
EBIT margin serves as a key indicator of a company’s operational efficiency and profitability. By understanding the fundamentals of EBIT margin and its significance, businesses can identify areas for improvement, make informed financial decisions, and strive for sustainable growth in today’s competitive business environment.







