Convertible bonds are a type of hybrid security that combines features of both bonds and stocks. They are debt instruments issued by corporations that can be converted into a predetermined number of the issuer’s common stock shares at the bondholder’s discretion during a specified time period. Essentially, they offer investors the opportunity to participate in potential stock price appreciation while also providing fixed income like traditional bonds.
How do they work?
- Convertible bonds function similarly to regular bonds, paying fixed interest payments at regular intervals until maturity.
- However, they also come with the option to convert the bond into a predetermined number of common stock shares of the issuing company.
- The conversion ratio determines how many shares the bondholder will receive for each bond converted.
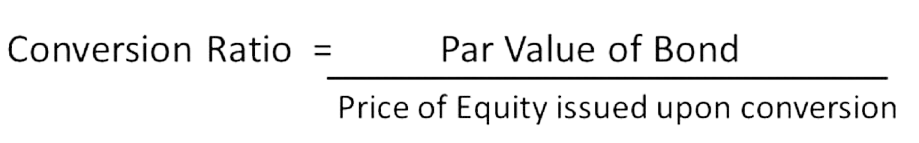
- Bondholders typically exercise this conversion option when the market price of the underlying stock exceeds a certain threshold, making it more profitable to convert the bond into equity rather than holding onto the bond.
Who issues convertible bonds and why?
Convertible bonds are primarily issued by corporations, especially those with growth potential and higher risk profiles. Companies may issue convertible bonds as a way to raise capital at a lower cost compared to issuing traditional equity. They provide issuers with the flexibility to attract investors seeking both fixed income and potential equity upside.
Who invests in convertible bonds and why?
Institutional investors, hedge funds, and individual investors may invest in convertible bonds.
Investors are attracted to convertible bonds because they offer a fixed income stream with the potential for capital appreciation if the underlying stock price rises.
They provide a way to participate in the growth of a company’s stock while still having downside protection in the form of fixed interest payments.
What are the key factors that affect the value of a convertible bond?
- The price and volatility of the underlying stock: Higher stock prices and volatility increase the value of the conversion option.
- Interest rates: Lower interest rates generally increase the value of bonds, including convertible bonds.
- Time to maturity: The longer the time until maturity, the greater the opportunity for the stock price to appreciate, increasing the bond’s value.
- Credit quality of the issuer: Investors assess the creditworthiness of the issuer to determine the bond’s risk and potential return.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of convertible bonds for both issuers and investors?
For issuers:
- Advantages:
- Lower cost of capital compared to issuing traditional equity.
- Ability to attract investors seeking both fixed income and equity upside.
- Potential to reduce dilution of existing shareholders compared to issuing common stock.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential dilution if bondholders convert their bonds into equity.
- Complex accounting treatment compared to traditional debt issuance.
For investors:
- Advantages:
- Potential for capital appreciation if the underlying stock price increases.
- Downside protection through fixed interest payments.
- Diversification benefits due to hybrid nature of the security.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited upside potential compared to holding the underlying stock directly.
- Exposure to credit risk of the issuer.
- Complexity in evaluating the bond’s value due to the interplay of bond and equity characteristics.
Investment Strategies with Convertible Bonds
- Hedging Strategies: Investors can use convertible bonds to hedge against market volatility. When stock prices fall, the bond aspect of a convertible bond provides some protection. When stock prices rise, conversion becomes advantageous.
- Arbitrage Opportunities: Sophisticated investors might explore arbitrage opportunities by exploiting price discrepancies between a convertible bond and the underlying stock.
- Balanced Investment: For those looking for a middle ground between stocks and bonds, convertible bonds offer a unique combination that features income, potential appreciation, and lower volatility compared to common stocks.
Conclusion
Convertible bonds offer a compelling option for both issuers and investors, providing a flexible financing tool for companies and a dual-benefit investment opportunity for investors. Whether aiming for protection against downside risk, potential for appreciation, or portfolio diversification, convertible bonds can play a strategic role in achieving various financial goals. Investors should carefully consider the terms of the bond and the performance potential of the issuing company to maximize the benefits of their investment in convertible bonds.