Cash Flow Per Share (CFPS) serves as a crucial metric in evaluating a company’s financial health and performance. Let’s delve into the significance of CFPS, how it’s calculated, its importance, limitations, and how investors can leverage this metric to make informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Cash Flow Statement: A Tool for Quantitative Decision-Making
The cash flow statement, one of the three fundamental financial statements (alongside the income statement and balance sheet), provides critical insights into a company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health. This statement records the cash inflows and outflows from operations, investing, and financing activities over a specific period. By analysing these numbers, stakeholders can make informed, quantitative decisions about a company’s operational efficiency, investment viability, and funding strategy.
What is Cash Flow Per Share?
CFPS is a financial metric that measures the amount of cash generated by a company per outstanding share of its common stock.
It indicates the cash flow generated by each share of stock, providing insights into the company’s ability to generate cash from its core operations.
How is Cash Flow Per Share Calculated?
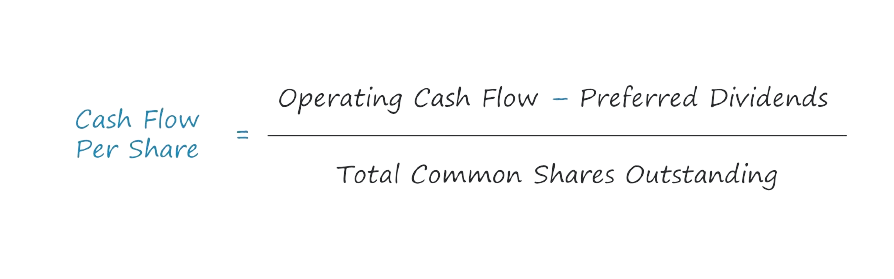
Operating Cash Flow (OCF) → OCF measures the net cash generated from a company’s core operations within a specified period. The operating cash flow (OCF) metric, or cash flow from operations, is meant to represent the cash flows generated from the core, recurring operations of a company.
Preferred Dividends → Dividend issuances paid to the owners of a company’s preferred stock, which hold precedence over common shareholders.
Total Common Shares Outstanding → The total weighted average number of common shares outstanding, i.e. each share is weighted by the proportion of the given fiscal year in which the share was “outstanding”.
Why is Cash Flow Per Share Important?
- CFPS provides a clearer picture of a company’s financial health than traditional earnings per share (EPS), as it focuses on actual cash generated rather than accounting profits.
- It helps investors assess the sustainability of dividend payments, the ability to reinvest in the business, and the company’s overall financial strength.
Limitations of Cash Flow Per Share
- CFPS may not fully capture the quality of cash flows or the company’s capital expenditure requirements.
- It can be manipulated through accounting practices, such as aggressive revenue recognition or delaying capital expenditures.
- CFPS does not account for changes in working capital, which can impact a company’s liquidity position.
How Can Investors Use Cash Flow Per Share?
Investors can use CFPS to compare companies within the same industry or sector, providing insights into relative valuation and performance.
CFPS can help investors identify companies with strong cash flow generation capabilities, which may be better positioned to weather economic downturns or pursue growth opportunities.
By analysing trends in CFPS over time, investors can assess the company’s ability to sustain cash flow growth and return value to shareholders.
Where Can Investors find Cash Flow Per Share Information?
CFPS information can typically be found in a company’s financial statements, including the cash flow statement and earnings reports. Investors can also access CFPS data through financial websites, investment research platforms, and stock market databases.
Conclusion
Cash Flow Per Share (CFPS) is a valuable metric for investors seeking to evaluate a company’s financial strength and performance. By understanding how CFPS is calculated, its importance, limitations, and how investors can utilize this metric, individuals can make more informed investment decisions and build a well-rounded investment portfolio.







