NSE: FEDERALBNK
Federal Bank (FBL) was established on April 23, 1931, and is headquartered in Aluva, Kerala. Originally named Travancore Federal Bank Limited, it was renamed The Federal Bank Limited in December 1949. The transformation of FBL began under the leadership of the late K.P. Hormis, who became its Chief Executive in 1945.1
Business operations:
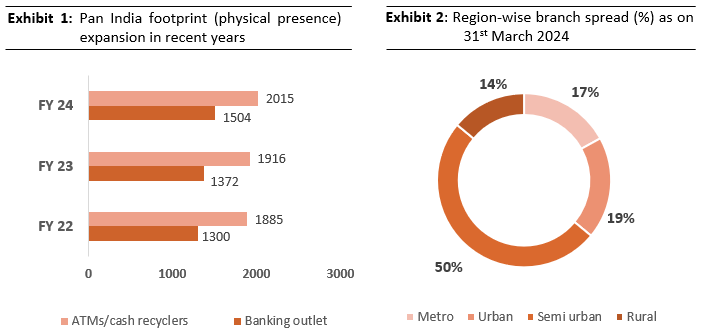
FBL operates across treasury, wholesale banking, retail banking, and other banking services. It serves over 1.82 crore customers through a network of 1,504 branches and 2,015 ATMs/Recyclers across India (as of March 31, 2024). FBL offers a variety of financial products such as internet and mobile banking, loans, deposits, insurance, and mutual funds.
As of September 2024, the revenue mix of FBL is dominated by its retail and commercial banking operations, which together account for a substantial 84.7% of the total revenue. Retail banking alone contributes the largest share, comprising 57.4% of the overall revenue. Treasury operations, which are integral to FBL’s asset and liability management, contribute 14.4% to the revenue. The remaining 1.1% of the revenue is derived from FBL’s other banking operations.
Physical presence:
FBL is a prominent private sector bank, primarily operating in South India. Roughly 70% of its branches are located in this region, with Kerala being its strongest market, accounting for 40% of its branch network and 30% of its loan portfolio; apart from that FBL currently has a physical presence across 26 states and 5 Union Territories in India, along with international representative offices in Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
Moreover, FBL has actively emphasized upon promotion of digital channels to further improve its reach. In FY24, a significant 94.3% of transactions were conducted digitally, representing a 74% year-on-year increase.
Financial Performance (FY 2023-24) 1
• Revenue: Net Interest Income: ₹8,293 crore, contributing approximately 73% of total income. Non-Interest Income: ₹3,079 crore, accounting for 27% of total income.
• Profit After Tax (PAT): FBL recorded its highest-ever PAT at ₹3,721 crore, marking a 24% year-on-year growth (FY 2022-23: ₹3,011 crore).
• Net Interest Income Growth: Grew by 27%, from ₹6,538 crore in FY 2022-23 to ₹8,312 crore in FY 2023-24.
• Net Advances: Reached ₹2,09,403 crore, showing a 20% increase from ₹1,74,447 crore in FY 2022-23.
• NPA Levels: Gross NPA: ₹4,529 crore (2.13% of Gross Advances). Net NPA: ₹1,255 crore (0.60% of Net Advances). Provision Coverage Ratio: 71.08% (excluding technical write-offs).
• Capital Adequacy: FBL maintained a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of 16.13%, well above the regulatory requirement of 11.50%.
FBL has a presence across 26 states and 5 Union Territories in India, even though bank operates primarily in South India, with 70% of its branches located there. Kerala is its strongest market, holding 40% of FBL’s branches and accounting for 30% of its loans. While Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu contribute 21% and 13% of loans respectively, FBL is actively expanding into other states, with plans to open 80-100 new branches to diversify its business and attract deposits from a wider geographic area. FBL also operates representative offices in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, serving its international clientele; it also has an International Financial Service Centre (IFSC) Banking unit (IBU) in Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City).
Source: annual report
FBL has a well-distributed network of branches across metro, urban, semi-urban, and rural areas to meet the needs of various customers. In FY 23, 52% of its branches were in metro areas, 18% in urban regions, 13% in semi-urban locations, and 17% in rural areas.
In FY 2023-24, the overall metro coverage of FBL is 50%, further the rural branch share stands at 19%, and urban branch share at 17%.
FBL added 141 new banking outlets in FY24, with a significant portion located in areas with high potential, particularly in rural and semi-urban regions. Further going forward the bank aims to leverage digital channels to complement the branch expansion, particularly in rural areas where physical access might be limited.







