Peer analysis of Federal Bank, IndusInd Bank, and IDFC First Bank, three mid-sized private sector banks with comparative market capitalizations as of FY24.1 9 11
Revenue
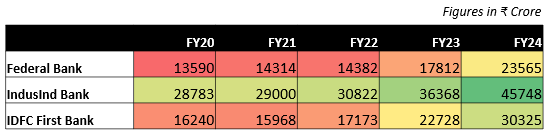
• Federal Bank reported consistent growth, with revenue increasing from ₹13,590 crore in FY20 to ₹23,565 crore in FY24, achieving a CAGR of 16.9%. This performance was supported by a focus on high-margin retail products, stable Net Interest Margins, and an expanding credit portfolio driven by digital adoption and physical network growth.
• IndusInd Bank maintained steady growth, with revenue rising from ₹28,783 crore in FY20 to ₹45,748 crore in FY24, reflecting a CAGR of 12.9%. The bank sustained a larger revenue base throughout this period.
• IDFC First Bank reported the highest revenue growth, with a CAGR of 21.7%, as revenue increased from ₹16,240 crore in FY20 to ₹30,325 crore in FY24. This growth was driven by a shift from wholesale and infrastructure financing to a retail-focused model, following its merger with Capital First. Retail assets grew from 37% of total funded assets in FY20 to 63% by FY21. The bank expanded its retail loan portfolio, strengthened its retail deposit base, and used Capital First’s expertise, branch network, and technology to enhance operations and customer outreach.
Net Interest margin
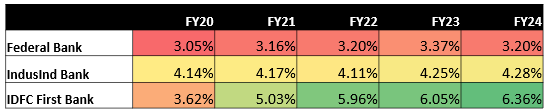
• Federal Bank’s NIM has remained relatively stable, ranging between 3.05% and 3.37% from FY 20 to 24. Further, NIM is projected to improve to 3.5 to 4% by FY27, driven by the bank’s focus on increasing CASA deposits and high-yielding retail loans.
• IndusInd Bank’s NIM has also shown stability, fluctuating between 4.11% and 4.28%. It is further expected to remain stable, benefiting from its established wholesale banking model.
• In contrast, IDFC First Bank has experienced a significant improvement in its NIM, rising from 3.62% in FY20 to 6.36% in FY24. This increase is partly due to a focus on high-margin retail products. Additionally, after merging with Capital First, the bank’s Current Account Savings Account (CASA) deposits have grown significantly, now making up nearly 50% of total deposits. Since CASA deposits are a low-cost source of funds, this has helped improve the bank’s NIM and profitability.
Net NPA
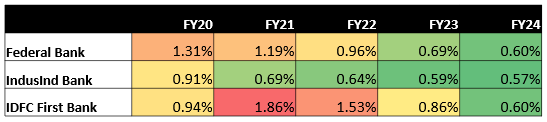
• Federal Bank has consistently reduced its Net NPA ratio, from 1.31% in FY20 to 0.60% in FY24. The bank’s GNPA ratio is expected to remain stable at around 2.1% over the next three years, supported by its proactive credit monitoring systems and focus on retail loans, which are less prone to defaults. Federal Bank’s diversification efforts to reduce concentration in South India will further strengthen its asset quality.
• IndusInd Bank has also shown a steady decline in its Net NPA ratio, from 0.91% in FY20 to 0.57% in FY24. It is projected to remain within a manageable range, but its reliance on wholesale loans could expose it to sectoral risks.
• IDFC First Bank experienced a significant spike in its Net NPA ratio to 1.86% in FY21 but has since made substantial progress in reducing it to 0.60% in FY24. Even though, all three banks have demonstrated a positive trend in reducing their Net NPAs, indicating improved asset quality and risk management practices. However, IDFC First Bank’s past performance suggests that its asset quality is more volatile compared to the other two banks.
Capital adequacy ratio
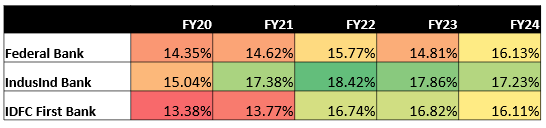
• Federal Bank has consistently maintained a strong CAR, ranging from 14.35% to 16.13%, well above the RBI’s minimum standard of 11.5%. While there was a minor dip in FY23, the bank recovered well in the subsequent year.
• IndusInd Bank, despite starting with a lower CAR of 15.04% in FY20, significantly improved its position, reaching a peak of 18.42% in FY22. Although the CAR has slightly decreased since then.
• IDFC First Bank also experienced a notable improvement in its CAR, increasing from 13.38% to a high of 16.82% in FY23. Similar to IndusInd Bank, a minor decrease was observed in FY24
In comparison, Federal Bank’s CAR has shown more stability, while IndusInd Bank and IDFC First Bank have experienced fluctuations. Overall, all three banks maintain a healthy CAR.
CASA Ratio
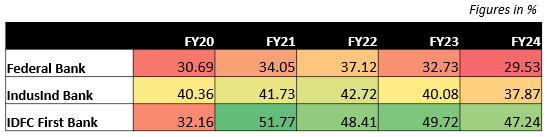
• Federal Bank witnessed a steady increase in its CASA ratio from FY20 to FY22, reaching a peak of 37.12%. However, the ratio declined in the subsequent two years, ending at 29.53% in FY24. This decline can be attributed to the rising interest rate environment, led by a stable repo rate at 6.5%. As interest rates increased, and shifting preference towards term deposits.
• IndusInd Bank maintained a consistent CASA ratio between FY20 and FY22, ranging from 40.36% to 42.72%. The ratio experienced a slight decline in the following two years, ending at 37.87% in FY24.
• IDFC First Bank saw a significant improvement in its CASA ratio, increasing from 32.16% in FY20 to a high of 51.77% in FY21. While the ratio declined slightly in FY22, it remained relatively stable in the following two years, ending at 47.24% in FY24.In comparison to its peers, IDFC First Bank has demonstrated the most significant improvement in its CASA ratio, indicating a growing preference for its offerings
Return on Asset
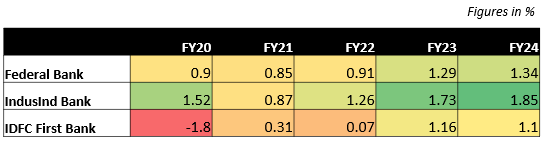
•Federal Bank witnessed a steady improvement in its ROA, increasing from 0.9% in FY20 to 1.34% in FY24. This indicates that the bank has become more efficient in utilizing its assets to generate profits. FBL‘s ROA is forecasted to improve from 1.34% in FY24 to 1.5% by FY27, driven by higher fee income and operational efficiency.
• IndusInd Bank experienced a significant decline in its ROA in FY21, dropping from 1.52% in FY20 to 0.87%. However, the bank recovered well in subsequent years, reaching an ROA of 1.85% in FY24. This improvement suggests that the bank has implemented strategies to enhance its profitability. Going forward, bank’s ROA is expected to stabilize around 1.85%.
• IDFC First Bank experienced a significant loss in FY20, resulting in a negative ROA of -1.8%. However, the bank’s performance improved significantly in the following years, with the ROA reaching 1.1% in FY24. This turnaround indicates that the bank has taken effective measures to improve its profitability.
In comparison to its peers, Federal Bank and IndusInd Bank have demonstrated a consistent improvement in their ROA, indicating strong financial performance. IDFC First Bank, while experiencing a challenging FY20, has shown a remarkable turnaround in recent years.
Earning per Share
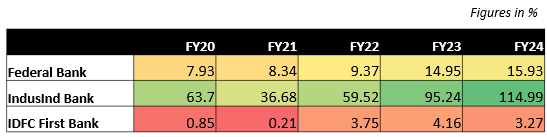
• Federal Bank witnessed a steady increase in its EPS, from 7.93 in FY20 to 15.93 in FY24. This indicates that the bank’s profitability has been consistently improving over the years. IndusInd Bank experienced a significant decline in its EPS in FY21, dropping from 63.7 in FY20 to 36.68. However, the bank recovered well in subsequent years, reaching an EPS of 114.99 in FY24. This is significantly higher than the EPS of the other two banks, indicating a strong performance.
• IndusInd Bank experienced a significant decline in its EPS in FY21, dropping from a high of 63.7 in FY20 to 36.68. This sharp fall is attributed to various factors, such as economic headwinds, loan quality issues, or changes in accounting standards. However, the bank demonstrated a remarkable recovery in subsequent years, reaching an EPS of 114.99 in FY24.
• IDFC First Bank experienced a significant decline in its EPS in FY21, dropping from 0.85 in FY20 to 0.21. However, the bank recovered well in subsequent years, reaching an EPS of 4.16 in FY23. This improvement indicates that the bank has taken effective measures to improve its profitability.
In comparison to its peers, Federal Bank and IndusInd Bank have demonstrated a consistent improvement in their EPS, indicating strong financial performance. IndusInd Bank, in particular, stands out with its significantly higher EPS, reflecting its strong profitability.







