India’s economy is picking up pace in the second half of the 2024-25 financial year, thanks to government tax cuts and lower interest rates. According to the latest RBI Bulletin, several indicators like vehicle sales, air travel, steel consumption, and GST E-way bills show that economic activity is improving.
Signs of Economic Growth
One of the strongest signs of recovery is in the manufacturing sector, where industrial production has increased. The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) for January 2025 confirms that factory activity is expanding.
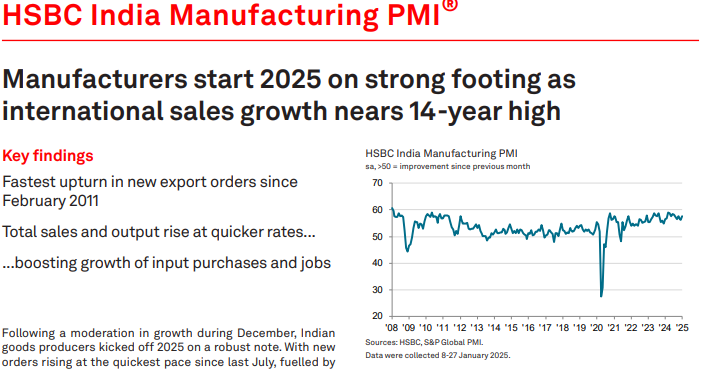
Source: S&P Global
In rural areas, tractor sales and fuel consumption have gone up, showing that farming activity and overall economic engagement are increasing. Meanwhile, air passenger traffic is growing, signaling a rebound in the services sector and higher consumer confidence.
Source: Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell
Even Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) companies have reported a surge in sales. Rural sales grew by 9.9% in Q3 FY25, compared to 5.7% in the previous quarter. Urban areas also saw improvement, with sales rising by 5%, compared to just 2.6% earlier. This suggests that people are spending more, both in villages and cities.
What’s Driving the Recovery?
A few key factors are helping the economy bounce back:
- Tax Cuts & Lower Interest Rates – The Union Budget 2025-26 announced major income tax relief, putting more money in people’s hands and boosting spending. At the same time, the RBI cut its key interest rate (repo rate) by 25 basis points to 6.25%, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers.
- Rural & Urban Demand – Strong agricultural performance has increased rural earnings, while lower inflation has improved urban spending power. Together, these are supporting industrial growth and retail consumption.
- Positive Growth Forecast – The RBI expects India’s GDP to grow by 6.6% in the January-March 2025 quarter, an improvement from 5.4% in the July-September 2024 quarter. For the full 2025-26 financial year, growth is projected at 6.7%, aligning with government estimates.
Inflation and Global Risks
Inflation is coming down, which is a good sign. In January 2025, inflation dropped to 4.3% from 5.22% in December, while food inflation declined from 7.7% to 5.7%. However, the RBI warns that global trade tensions, rising energy prices, and extreme weather conditions could create risks for future growth.
Conclusion
Overall, the Indian economy is showing strong signs of recovery. With higher consumer spending, government support, and a better business environment, the outlook for 2025 remains positive. However, policymakers will need to remain cautious about external challenges that could impact long-term growth.







