Written By: Eklavya Guneja
Ever wondered why some traders seem to predict market moves with uncanny accuracy? It’s not magic, it’s data. And two of the most powerful indicators they use are Open Interest (OI) and Volume Analysis. If you’re new to trading, buckle up! This guide will break it down in the simplest way possible with relatable examples.
What is Open Interest (OI)?
Imagine a cricket match where everyone bets on whether Virat Kohli will score a century. Every new bet placed is like an open contract. In the stock market, Open Interest (OI) represents the total number of outstanding options or futures contracts that have not yet been settled.
– If OI is increasing, new money is flowing into the market, meaning more traders are opening positions.
– If OI is decreasing, traders are closing out positions, signaling a potential reversal or lack of interest.
Example:
Rohit sees that the Nifty 50 Call Option (strike price 23,000) has an increasing OI. This means more traders believe Nifty will go up. On the other hand, if OI is decreasing, it might indicate that traders are closing positions, expecting a fall or stagnation.
Understanding Volume in Trading
Volume tells you how many contracts (futures or options) were traded in a day. It shows the activity level and interest in a particular stock or index.
– High volume with increasing price = Strong trend confirmation
– High volume with decreasing price = Possible reversal ahead
– Low volume = Lack of conviction among traders
Example:
Priya is tracking Reliance Industries’ futures. She sees a sudden spike in volume while the price is rising – this suggests that strong hands are entering, and the uptrend may continue.
Open Interest, Volume & Market Sentiment Table
Here’s how different combinations of OI and volume affect market sentiment:
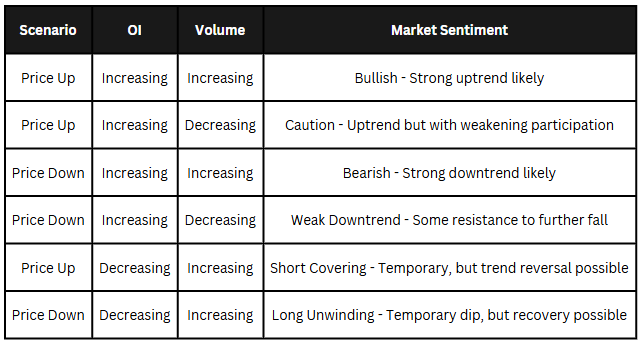
By analyzing these patterns, traders can make more informed decisions instead of blindly following price movements.
Understanding the Put-Call Ratio (PCR)
The Put-Call Ratio (PCR) is one of the most widely used indicators to gauge market sentiment. It helps traders determine whether the market is leaning towards bullishness or bearishness based on the volume and open interest of put and call options.
How is PCR Calculated?
PCR is calculated in two main ways:
- Based on Volume:

- Based on Open Interest:
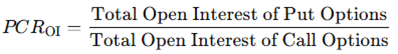
Both methods are valid, but PCR based on Open Interest is considered more reliable for longer-term analysis, while PCR based on Volume is better for intraday sentiment.
Interpreting the PCR Value
– PCR < 0.5 → Bullish Market Sentiment
If the PCR is below 0.5, it indicates that call options are being traded more than put options, suggesting that traders are optimistic about the market moving up.
– PCR between 0.5 and 1.0 → Neutral to Slightly Bearish
This is the normal range. If PCR is around 0.7–0.8, it shows a balanced market with a slight bearish tilt.
– PCR > 1.0 → Bearish Market Sentiment
If the PCR exceeds 1.0, it means more puts are being traded than calls, signaling a bearish outlook. A high PCR often suggests that traders are hedging against potential declines.
Final Thoughts
Open Interest and Volume Analysis are like a trader’s compass – helping you navigate the markets with confidence. By understanding how these factors interact and combining them with tools like the Put-Call Ratio, you can make smarter, data-backed trading decisions.
So, next time you analyze a trade, don’t just look at the price – check OI, volume, and PCR to get the full picture!
Happy learning, and here’s to making finance-friendly and approachable!






