Dividends are payments a company makes to share profits with its stockholders. They’re one of the ways investors can earn a regular return from investing in stocks. Dividends can be paid out in cash, or they can come in the form of additional shares.
What is dividend yield?
- Dividend yield is a financial metric that indicates the percentage return on investment generated by a stock through dividends.
- In simpler terms, dividend yield tells you how much money you’ll earn each year relative to the price you paid for a stock.
How is dividend yield calculated?
To calculate dividend yield, you take the annual dividend per share (the total amount of dividends paid out to shareholders over a year) and divide it by the current market price per share of the stock. The result is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage.

For example: If a stock pays an annual dividend of Rs.2 per share and its current market price is Rs.50 per share, the dividend yield would be (2/50) X 100 = 4%.
Why is dividend yield important to investors?
- Dividend yield is important to investors because it provides insight into how much income they can expect to receive from their investment in a particular stock relative to its current price.
- It helps investors assess the income-generating potential of a stock and compare it to other investment opportunities, such as bonds or growth stocks.
What factors influence dividend yield?
- Several factors can influence dividend yield including the company’s profitability, cash flow, dividend policy and market conditions.
- Generally, companies with stable earnings and a history of consistent dividend payments tend to have higher dividend yields. Economic factors, industry trends, and changes in interest rates can also impact dividend yields.
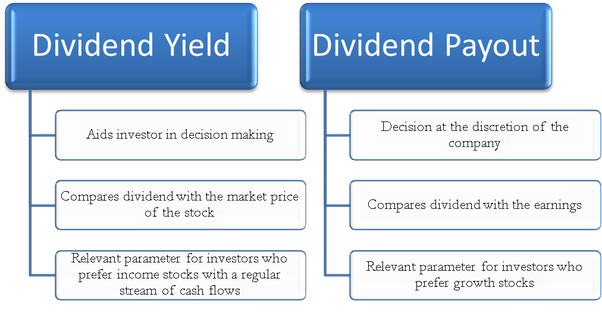
How does dividend yield differ from dividend pay-out ratio?
- While dividend yield measures the percentage return on investment generated by a stock through dividends relative to its current market price, the dividend pay-out ratio measures the proportion of earnings paid out to shareholders as dividends.
- In other words, dividend yield focuses on the income generated by dividends relative to the stock price, while the dividend pay-out ratio focuses on the portion of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends.
What are the potential advantages and limitations of high dividend yield stocks?
- High dividend yield stocks can offer investors a steady stream of income making them attractive for those seeking regular cash flow from their investments.
- However, high dividend yields can also indicate that the stock price has declined, which may be a sign of financial distress or limited growth prospects for the company. Additionally, high dividend payments may limit the company’s ability to reinvest in growth opportunities or weather economic downturns. Investors should carefully consider both the potential benefits and risks associated with high dividend yield stocks.
Conclusion
Understanding dividend yield is not merely about crunching numbers—it’s about grasping the essence of income generation in investment. Armed with the knowledge presented in this guide, investors can navigate the complex terrain of dividend investing with clarity and purpose, leveraging dividend yield as a valuable tool in their quest for financial success.







